IPSEC between CableFree router and a Shrew client
Overview
This article shows how to connect Shrew Ipsec client to RadioOS Ipsec server.
Shrew client works on both Windows (without need of L2TP) and Linux, see more details in their website
RadioOS Configuration
Lets assume that we already have IP connectivity between client and server. Client's IP address will be 10.5.101.20 and servers IP address will be 10.5.101.3.
IPSec configuration
/ip ipsec peer add address=10.5.101.20/32 auth-method=pre-shared-key exchange-mode=main\ secret=123 hash-algorithm=md5 enc-algorithm=3des generate-policy=yes
Since we assume that it is Road-Warrior setup, we do not know from where client will be connecting, so generate-policy=yes should be set.
The rest of the configuration is default
Shrew client configuration
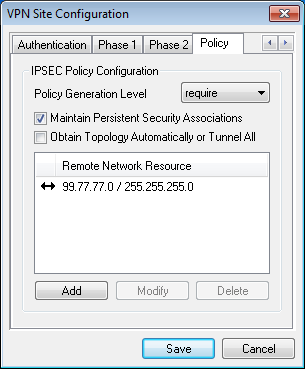
Now we need to match configuration on Shrew client. And assume that we want to reach remote network 99.77.77.0/24 located behind router from Shew client
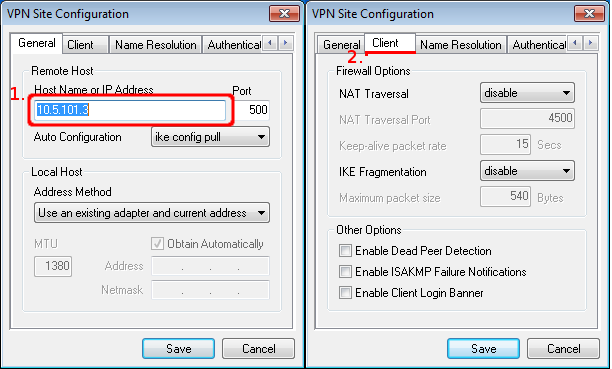
- On the first configuration tab ("General") we simply specify server's IP address.
- On the second tab ("Client") disable any features that you do not want to use. In this case we are not using NAT-T, DPD, etc. So all of them are disabled.
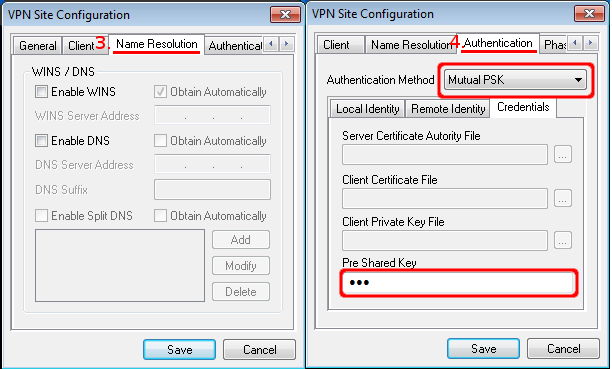
- On the third tab ("Name Resolution") we disable everything since these options are used by modecfg, which is not supported on ROS.
- On the fourth tab In our case we are using pre shared key, so choose Mutual PSK and enter pre shared key.
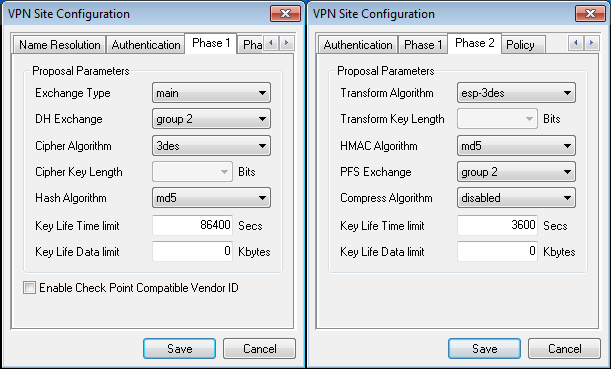
- On "Phase1" and "Phase2" tabs we match configuration to the RadioOS config. Phase1 should match /ip ipsec peer config and Phase 2 should match /ip ipsec proposal config
- And the last one we manually set which network we want to reach so that Ipsec can generate proper policies.
Here is the whole Shew config, you can import it in your client
n:version:2 n:network-ike-port:500 n:network-mtu-size:1380 n:network-natt-port:4500 n:network-natt-rate:15 n:network-frag-size:540 n:network-dpd-enable:0 n:client-banner-enable:0 n:network-notify-enable:0 n:client-wins-used:0 n:client-wins-auto:1 n:client-dns-used:0 n:client-dns-auto:0 n:client-splitdns-used:0 n:client-splitdns-auto:0 n:phase1-dhgroup:2 n:phase1-life-secs:86400 n:phase1-life-kbytes:0 n:vendor-chkpt-enable:0 n:phase2-life-secs:3600 n:phase2-life-kbytes:0 n:policy-nailed:1 n:policy-list-auto:0 s:network-host:10.5.101.3 s:client-auto-mode:pull s:client-iface:direct s:network-natt-mode:disable s:network-frag-mode:disable s:auth-method:mutual-psk s:ident-client-type:address s:ident-server-type:address s:ident-client-data:10.5.101.20 s:ident-server-data:10.5.101.3 b:auth-mutual-psk:MTIz s:phase1-exchange:main s:phase1-cipher:3des s:phase1-hash:md5 s:phase2-transform:esp-3des s:phase2-hmac:md5 s:ipcomp-transform:disabled n:phase2-pfsgroup:2 s:policy-level:require s:policy-list-include:99.77.77.0 / 255.255.255.0
Check Connectivity
[admin@CableFree] /ip ipsec remote-peers> print 0 local-address=10.5.101.3 remote-address=10.5.101.20 state=established side=responder established=44m3s
- IPSec should show intalled-sa,
[admin@CableFree] /ip ipsec installed-sa> print
Flags: A - AH, E - ESP, P - pfs
0 E spi=0x476464 src-address=10.5.101.20 dst-address=10.5.101.3
auth-algorithm=md5 enc-algorithm=3des replay=4 state=mature
auth-key="fae8bc2918fea03dac0b7c8b6db57c60"
enc-key="15627d42163ad1fd58ee7cdc80d971d334883dbd2d81c42c"
addtime=sep/27/2012 13:51:07 expires-in=15m32s add-lifetime=48m/1h
current-bytes=240
1 E spi=0x5D4BF3B9 src-address=10.5.101.3 dst-address=10.5.101.20
auth-algorithm=md5 enc-algorithm=3des replay=4 state=mature
auth-key="728b19191d2a111673298c07d1f459c2"
enc-key="c944c45447df5429860d3999e674e1689bb41527ec941c9a"
addtime=sep/27/2012 13:51:07 expires-in=15m32s add-lifetime=48m/1h
current-bytes=240
- And dynamically created policies
[admin@CableFree] /ip ipsec policy> print
Flags: X - disabled, D - dynamic, I - inactive
1 D src-address=10.5.101.20/32 src-port=any dst-address=99.77.77.0/24
dst-port=any protocol=all action=encrypt level=require ipsec-protocols=esp
tunnel=yes sa-src-address=10.5.101.3 sa-dst-address=10.5.101.20
proposal=default priority=2
2 D src-address=10.5.101.20/32 src-port=any dst-address=99.77.77.0/24
dst-port=any protocol=all action=encrypt level=require ipsec-protocols=esp
tunnel=yes sa-src-address=10.5.101.3 sa-dst-address=10.5.101.20
proposal=default priority=2
3 D src-address=99.77.77.0/24 src-port=any dst-address=10.5.101.20/32
dst-port=any protocol=all action=encrypt level=require ipsec-protocols=esp
tunnel=yes sa-src-address=10.5.101.20 sa-dst-address=10.5.101.3
proposal=default priority=2
Allow only encrypted traffic
We want local network behind the server to be reachable only by VNP users using encryption and drop other un-encrypted access. To do so we will need to set up firewall on the router.
First step is to allow ispec related packets. Rules allows also AH protocol and NAT-T port, which is not used in current setup but added for future use.
/ip firewall filter add chain=ipsec protocol=ipsec-esp add chain=ipsec protocol=ipsec-ah add chain=ipsec protocol=udp src-port=500 add chain=ipsec protocol=udp src-port=4500
Now we add the typical rules to allow established/related connections in input chain and jump to ipsec chain
/ip firewall filter add chain=input connection-state=established add chain=input connection-state=related add action=jump chain=input in-interface=WAN jump-target=ipsec
After decrypting ipsec packets they appear in IP firewall like regular packets. For more information see packet flow example.
Now the trick is to determine which packets with destination (99.77.77.0/24) arrived over the ipsec tunnel. To do that we use mangle to mark ESP packets
/ip firewall mangle
add action=mark-packet chain=prerouting in-interface=WAN new-packet-mark=\
ipsec-encrypted passthrough=no protocol=ipsec-esp
After packets are marked we can add firewall rules to accept encrypted packets and drop the rest
/ip firewall filter add chain=input in-interface=WAN packet-mark=ipsec-encrypted add action=reject chain=input dst-address=99.77.77.0/24
Do the same in forward chain
/ip firewall filter add chain=forward connection-state=established add chain=forward connection-state=related add chain=forward in-interface=WAN packet-mark=ipsec-encrypted add action=reject chain=forward dst-address=99.77.77.0/24
Testing firewall
After setting firewall connect Shrew client and run ping from the client to destination network.
C:\Users\T>ping 99.77.77.1 -t Pinging 99.77.77.1 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 99.77.77.1: bytes=32 time=9ms TTL=64 Reply from 99.77.77.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64 Reply from 99.77.77.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64 Reply from 99.77.77.1: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=64
We can see in mangle and filters that packets are successfully matched and accepted
[admin@CableFree] /ip firewall mangle> print stats Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # CHAIN ACTION BYTES PACKETS 0 prerouting mark-packet 2 240 20 [admin@CableFree] /ip firewall filter> print stats chain=forward Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # CHAIN ACTION BYTES PACKETS 0 forward accept 0 0 1 forward accept 0 0 2 forward accept 1 500 25 3 forward reject 0 0
Now disconnect shrew client and you will notice that immediately ping throws an error that network is unreachable
Reply from 99.77.77.1: bytes=32 time=17ms TTL=64 Reply from 99.77.77.1: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=64 Reply from 99.77.77.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=64 Reply from 99.77.77.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=64 Request timed out. Reply from 10.5.101.3: Destination net unreachable. Reply from 10.5.101.3: Destination net unreachable. Reply from 10.5.101.3: Destination net unreachable. Reply from 10.5.101.3: Destination net unreachable. Reply from 10.5.101.3: Destination net unreachable.
And in firewall filtes you will see that last five packets are rejected by the reject rule.
[admin@CableFree] /ip firewall filter> print stats chain=forward Flags: X - disabled, I - invalid, D - dynamic # CHAIN ACTION BYTES PACKETS 0 forward accept 0 0 1 forward accept 0 0 2 forward accept 15 600 260 3 forward reject 300 5