What is 5G?

5G, the fifth generation of mobile networks, is fundamental to connected society, addressing the exponential growth in data traffic, massive device connectivity, and mission-critical applications. Standardised by 3GPP and aligned with ITU’s IMT-2020 requirements, 5G delivers connectivity for diverse use cases, including wearables, smart homes, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and ultra-high-speed media delivery. It accelerates the Internet of Things (IoT), supports real-time communications, and ensures ultra-high reliability for critical applications. The ITU, in collaboration with industry stakeholders, operators, manufacturers, and academia, finalised the performance requirements for 5G in 2020, enabling a robust ecosystem for global deployment.
The Aim of 5G
5G aims to provide seamless connectivity for any device and application, from low-power IoT sensors to high-bandwidth, low-latency services. Unlike previous generations, 5G is not a single radio-access technology but a portfolio of solutions, including:
-
5G New Radio (NR): A flexible air interface for extreme mobile broadband, supporting high-bandwidth scenarios and mission-critical communications with ultra-low latency.
-
Narrow-Band IoT (NB-IoT): Optimised for massive machine-type communications (MTC), offering deep coverage and high capacity for billions of devices, typically in sub-2 GHz bands.
-
LTE Integration: Evolved LTE (eLTE) ensures backward compatibility, allowing operators to leverage existing 4G infrastructure while transitioning to 5G.
5G addresses demands beyond those currently encountered, supporting diverse scenarios like enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), and massive MTC (mMTC).
4G to 5G Evolution
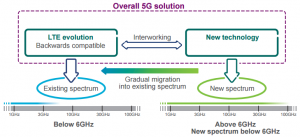
The transition from 4G LTE to 5G builds on the 3GPP roadmap, ensuring interoperability with legacy systems while introducing new capabilities. Key aspects include:
-
LTE Evolution: LTE-Advanced (Release 10–12) and LTE-Advanced Pro (Release 13–15) enhance 4G with features like carrier aggregation (up to 32 component carriers), higher-order MIMO (up to 64 antenna ports), and Licensed Assisted Access (LAA) for unlicensed spectrum. LTE remains integral, providing wide coverage in sub-6 GHz bands.
-
Dual Connectivity: 5G networks support dual connectivity between LTE (sub-6 GHz) and 5G NR (6–71 GHz), enabling user-plane aggregation for seamless data delivery across both interfaces.
-
Non-Standalone (NSA) and Standalone (SA) 5G: NSA 5G, introduced in Release 15 (2019), relies on LTE for control signalling, while SA 5G operates independently, offering full 5G capabilities. SA deployments are increasingly common, enhancing network slicing and URLLC.
-
Spectrum Flexibility: Operators can repurpose LTE spectrum for 5G NR, ensuring a smooth transition. Dynamic spectrum sharing (DSS) allows LTE and 5G to coexist in the same band, critical for operators with limited spectrum.
LTE continues to provide robust coverage, while 5G NR expands into higher bands (e.g. mmWave) for ultra-high speeds and new use cases, supported by CableFree LTE and 5G solutions compliant with Release 18 (2024).
Key 5G Capabilities
5G extends far beyond 4G, addressing diverse requirements through advanced technologies:
Massive System Capacity
-
Data Growth: With mobile data traffic projected to grow exponentially, 5G delivers data at a lower cost per bit, leveraging techniques like carrier aggregation, advanced MIMO, and small cell densification.
-
Energy Efficiency: 5G networks reduce energy per bit through optimised protocols, sleep modes, and renewable-powered base stations, supporting sustainable deployments.
-
Massive IoT: NB-IoT and LTE-M support billions of low-data-rate devices, with enhanced signalling and connection management to ensure security and scalability.
Very High Data Rates Everywhere
-
Peak Rates: 5G NR supports peak data rates exceeding 20 Gbps in ideal conditions (e.g. mmWave in dense urban areas).
-
Consistent Performance: Delivers 100–500 Mbps in urban/suburban areas and at least 10 Mbps in rural regions, ensuring equitable access.
-
mmWave and Sub-6 GHz: Combines high-capacity mmWave (24–71 GHz) for dense areas with sub-6 GHz for broader coverage.
Very Low Latency
-
URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication): 5G achieves end-to-end latency of 1 ms or less for applications like autonomous driving, industrial automation, and AR/VR.
-
Edge Computing: Multi-access edge computing (MEC) distributes processing near the air interface, reducing latency and enabling real-time services.
Ultra-High Reliability and Availability
-
Reliability: 5G supports 99.9999% packet delivery success within 1 ms for critical applications like traffic safety and smart grids.
-
Network Slicing: Creates dedicated virtual networks for specific use cases, ensuring consistent quality of service (QoS).
Low Device Cost and Energy Consumption
-
IoT Devices: NB-IoT and LTE-M devices are optimised for low cost and multi-year battery life, supporting massive deployments of sensors and actuators.
-
RedCap Devices: Release 17 (2022) introduced reduced-capability (RedCap) NR devices, balancing cost and performance for mid-tier IoT applications.
Energy-Efficient Networks
-
Operational Efficiency: Energy-efficient base stations and network designs reduce operational costs and support off-grid deployments using solar power.
-
Sustainability: 5G aligns with operators’ goals for resource-efficient networks, minimising environmental impact.
For More Information
Please Contact Us for more information on 5G and IMT-2020.
You must be logged in to post a comment.