How to achieve Remote Management of CableFree LTE CPEs using TR-069
TR-069 defines the generic requirements of the CPE WAN Management Protocol (CWMP) methods which can be applied to any TR-069 CPE. It is intended to support a variety of different functionalities to manage a collection of CPE, including the following primary capabilities:
- Auto-configuration and dynamic service provisioning
- Software/firmware image managementStatus and performance monitoring
- Diagnostics
The ability to manage the home network remotely has a number of benefits including reducing the costs associated with activation and support of broadband services, improving time-to-market for new products and services, and improving the user experience. If TR-069 defines the generic methods for any device, other documents (such as this one) specify the managed objects, or data models, which are collections of objects and parameters on which the generic methods act to configure, diagnose, and monitor the state of specific devices and services.
An Auto Configuration Server is an end-to-end TR-069 service fulfillment and device provisioning solution that lets you manage devices and services over xDSL, PON, WiMAX, LTE, Cable and FTTH.
What is TR-069?
![]()
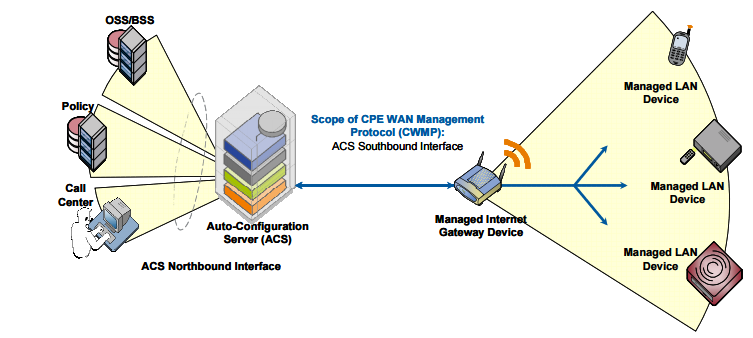
The CPE WAN (CWMP) Management Protocol, published by The Broadband Forum as TR-069, specifies a standard communication mechanism for the remote management of end-user devices. It defines a protocol for the secure auto-configuration of a TR-069 device and incorporates other management functions into a common framework. This protocol simplifies device management by specifying the use of an auto configuration server (ACS) to perform remote, centralized management of customer premises equipment (CPE).
 Who created it and why?
Who created it and why?
In 2004, The Broadband Forum (formerly The DSL Forum) released the CPE WAN Management Protocol, which is more commonly known as TR-069. This protocol standardizes the wide area network (WAN) management of CWMP devices. TR-069 gives broadband service providers a framework and common language to remotely provision and manage these devices, which are usually in a home network, regardless of device type or manufacturer.
TR-069 supports a variety of functionalities to manage CPEs and has the following primary capabilities:
- Auto-configuration and dynamic service provisioning
- Software/firmware management
- Status and performance monitoring
- Diagnostics
TR-069 is a specific technical report from Broadband Forum; however, the term is commonly used to refer to associated reports and extensions, including TR-106, TR-098, TR-104, TR-135, TR-140, and TR-111.See the Broadband Forum for the most up-to-date information.
How does it work?
TR-069 is a SOAP/HTTP-based protocol. Orders are sent between the device (CPE) and an auto configuration server over HTTP or HTTPS in the form of remote procedure calls (RPCs) and responses, with SOAP acting as the encoding syntax to transport RPCs. The CPE acts as the HTTP client and the ACS acts as the HTTP server.
The basic network elements required include:
- An auto configuration server (ACS): The management server on the network.
- Customer premises equipment (CPE): The device that is managed on the network
- DNS server: Used to resolve the URL that is required for the ACS and CPE to interact
- DHCP server: Can be used to assign an IP address to a device on the network. Well-known DHCP options can configure important parameters on the CPE, such as the ACS URL.
By specifying a variety of criteria, including provisioning parameters and vendor-specific information, an auto configuration server provisions a CPE or collection of CPEs.
How are tasks completed in a TR-069 environment?
In a TR-069 environment, tasks are completed through sessions. Each session consists of a series of remote procedure calls (RPC) between an ACS and the CPE. TR-069 uses HTTP or HTTPS and SOAP messaging, which allows messages to pass through firewalls and NAT gateways. TR-069 defines a generic mechanism by which an ACS can read or write parameters to configure a CPE and monitor CPE status and statistics.
What is an auto configuration server and why is it necessary?
TR-069 specifies communication between customer-premises equipment (CPE) and an auto configuration server. The auto configuration server acts as a management server for TR-069-enabled CPE. It is essentially the link between the subscriber’s devices in the home and the service provider’s customer service representative (CSR), support staff, operational support systems and business support systems (OSS/BSS). An auto configuration server enables you to automate provisioning and many management tasks for TR-069 devices, facilitating remote management.
Is it secure?
Most industry experts say “Yes”. The Broadband Forum designed the TR-069 security model to provide a high degree of security. The stated security goals of this protocol are below:
- Prevent tampering with the management functions of a CPE or ACS, or the transactions that take place between CPE and an ACS
- Provide confidentiality for the transactions that take place between CPE and ACS
- Allow appropriate authentication for each type of transaction
- Prevent theft of service
Secure socket layer (SSL) or transport layer security (TLS) should be used to encrypt traffic between CPE and an ACS. It is possible to use the protocol directly over a HTTP connection; however, some aspects of security will be sacrificed. When SSL/TLS is used, the CPE must authenticate the ACS using the ACS-provided certificate.
For More Information
For further information on the range of CableFree wireless networking products:
Please Contact Us

You must be logged in to post a comment.